A fire protection system is a crucial component of building safety designed to detect, control, and extinguish fires. It consists of various elements and technologies that work together to minimize the risk of fire-related damage and protect people's lives. Here are some key components and principles of a fire protection system:
 |
| Fire Protection system of building safety |
Fire Protection system of building safety
1- Fire Detection Systems:
- Smoke Detectors: These devices detect smoke particles in the air and trigger alarms when smoke is present.
- Heat Detectors: Heat detectors sense an increase in temperature caused by a fire and activate alarms.
- Flame Detectors: Flame detectors use sensors to detect the presence of flames or intense heat and trigger alarms.
2- Fire Alarm Systems:
When a fire is detected, fire alarm systems provide audible and visual alerts to notify building occupants of the emergency. These may include sirens, horns, strobe lights, and voice evacuation systems.
3- Fire Suppression Systems:
- Fire Sprinkler Systems: These systems use water sprinklers to control or extinguish fires. Sprinkler heads activate when a predetermined temperature is reached.
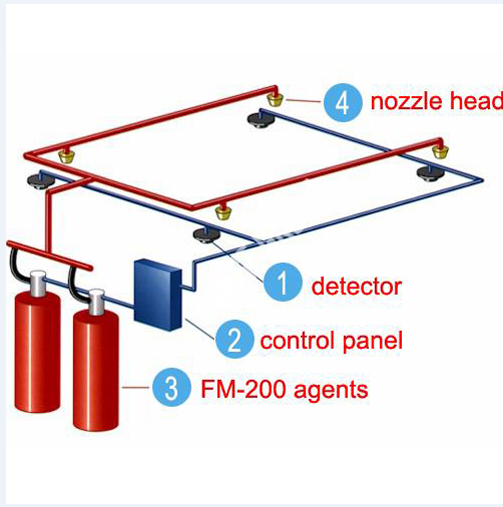
- Clean Agent Systems: Clean agents like FM-200, CO2, or inert gases are used to suppress fires without leaving residue or causing water damage.
- Foam Systems: Foam-based fire suppression systems are effective for fighting flammable liquid fires, such as those involving petroleum products.
4- Fire Extinguishers:
Portable fire extinguishers are strategically placed throughout a building to allow occupants to attempt to extinguish small fires before they escalate. Different types of extinguishers are used for various fire classes (e.g., Class A, B, C, D, or K).
5- Fireproofing Materials:
Fire-resistant building materials, such as fire-rated walls, doors, and fire-resistant coatings, help contain and slow the spread of fires.
6- Emergency Lighting:
Illuminated exit signs and emergency lighting systems ensure that occupants can safely evacuate a building during a fire, even if the power goes out.
7- Fire Safety Plans and Training:
Proper fire safety planning includes evacuation routes, assembly points, and training for building occupants on how to respond to fire emergencies.
8- Fire Department Connection (FDC):
FDCs are connections that allow firefighters to connect their hoses to the building's water supply, ensuring a steady source of water for firefighting efforts.
9- Fire Alarm Monitoring:
Many fire protection systems are connected to monitoring services that can alert local fire departments when an alarm is triggered, ensuring a faster response time.
10- Maintenance and Inspections:
Regular maintenance and inspections are essential to ensure that all components of the fire protection system are in working order and compliant with relevant codes and standards.
Read also Requirements for installation of Fire Sprinkler
Fire protection systems should be designed, installed, and maintained by qualified professionals in accordance with local building codes and regulations. These systems play a vital role in safeguarding lives and property, so their proper functioning is crucial in the event of a fire emergency.
Read also Fire Fighting Hazards Classification
Read also Zone Control Valve



0 Comments